Choose Your Language
Request a Quote
Electrical and Electronics
- Home
- Industries
- Electrical and Electronics
Our thermoplastics solutions can help provide the thermoplastic resin with the correct electrical, mechanical, thermal and chemical resistance properties you need for your application. From commodity to specialty materials for electronic housings, connectors, cables, batteries and more, we can help you find an ideal material solution that meets your sustainability, regulatory and performance goals.

Why are plastics used in the Electrical & Electronics End Market?
Plastic materials play an important role for several reasons:
What are some applications that use thermoplastics in the Electrical & Electronics End Market?
Plastics are used in E&E applications all around us; From the smartphones and tablets in our hands every day to the wires/cables and 5G transmitters that connect us all together. It is the connectors, switches, sensors, and control housings in your home, at the store, or in schools. And plastics can be found in applications helping to solve the emerging needs of Solar Energy infrastructure, EV Charging Stations, and improved batteries for home and portable use. Wherever safety and reliable performance is needed in the E&E market, plastics can be found.
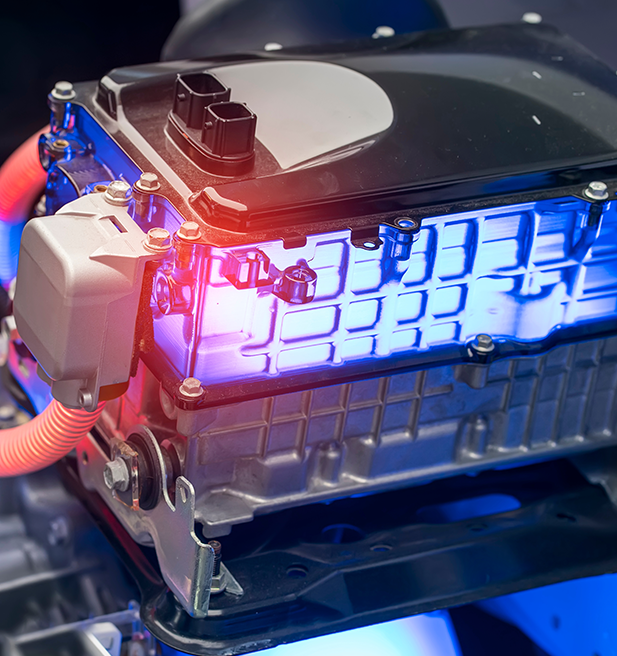
Batteries have a critical role in the electrical and electronics markets, particularly in the context of traditional lead acid batteries used in automotive and other motive applications to more advanced systems that support renewable energy, backup power systems, and electric vehicles. As our way of life evolves, with a more technology and sustainability-focused environment, demand for energy storage solutions is increasing.
What are the benefits of using plastic for batteries?
Plastics play a key role in the manufacturing of batteries, particularly in the form of battery casings, cell carriers, separators, cooling pipes, connectors, and insulators. These plastic components help to reduce the weight and cost of batteries while also improving their durability and resistance to damage.
What are common plastics used for batteries in the E&E industry?
Materials to consider for battery applications include:
|

What are the benefits of using plastic for connectors?
Connectors play a critical role in the electrical and electronics markets, facilitating the transfer of power and data between different components and systems. Plastics are commonly used in the manufacturing of connectors due to their excellent insulating properties, which help to prevent electrical arcing and short circuits.
In addition, plastic connectors are lightweight, durable, and resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for use in a wide range of applications, including industrial automation, consumer electronics, and automotive systems.
Furthermore, plastic connectors can be designed and customized to meet specific requirements, such as being compatible with different voltages, current ratings, and environmental conditions. This versatility has made plastic connectors a popular choice in the electric and electrical markets, contributing to the overall reliability and efficiency of these systems.
What are common plastics that can be used for E&E connectors?
Many common connectors are made from Nylon, PBT, and PET but those with unusual demand requirements may need higher-performance polymers like PPA, PPS, and PSU/PES.
Materials to consider for connectors include:
|

Cables are an essential component in the electrical and electronics markets, serving as a conduit for transmitting power and data between different components and systems. Plastics play a crucial role in the production of cables, particularly in the form of cable insulation and jacketing.
What are the benefits of using plastic for cables?
Plastic materials like PVC, polyethylene, and polypropylene are widely used in cable insulation due to their excellent insulating properties and ability to resist electrical breakdown. Plastic jacketing is also used to protect cables from damage and to provide additional insulation.
Moreover, plastics contribute to the overall flexibility and durability of cables, allowing them to withstand bending, stretching, and other stresses. This versatility has made plastic cables a popular choice in a wide range of applications, including telecommunications, power distribution, and industrial automation.
What are common plastics used for cables?
Materials to consider for cable applications include:

Plastics have a vital role in the production of consumer electronics, serving as a lightweight, durable, and cost-effective material for a wide range of applications. Plastic materials like, HIPS, ABS, and Polycarbonate are just a few of the commonly used materials in the manufacturing of consumer electronics due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent moldability, and resistance to impact and wear.
What are common applications in the consumer electronics market for plastic materials?
Plastics are used in the production of various components of consumer electronics, including cases, covers, buttons, and connectors. They also serve as excellent electrical insulators, making them ideal for use in circuit boards, displays, and other electronic components.
What are common plastics used for consumer electronics?
Materials to consider for consumer goods applications include:
|
|
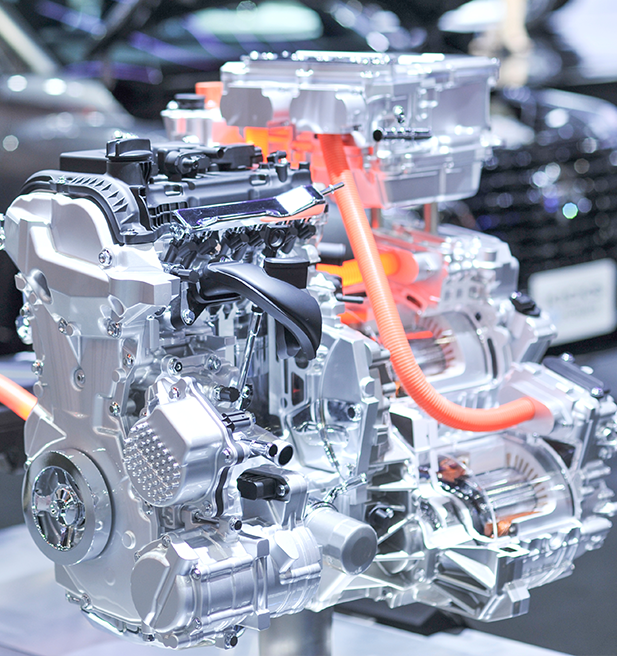
What are the common plastics being used in EV charging stations?
There are four major components to an external charging station, each using their own set of materials suited to performance requirements:
Additionally, EV charging stations are divided into two types: external/commercial usage and internal/home usage. While having similar needs overall, the minimum requirements for UV, weatherability and impact can be very different between the two types of stations as internal/home units are expected to see less wear/abuse over their service life.
Materials to consider for E-Motor applications include:
|
|
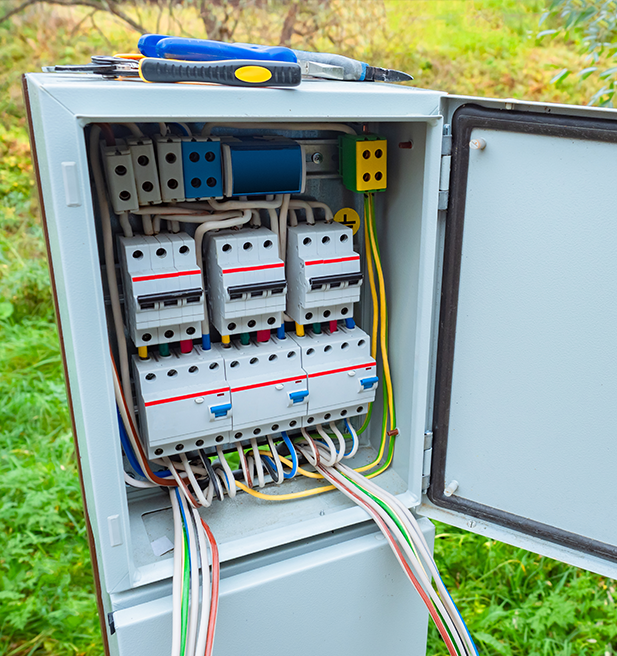
Housings are an essential component in the electrical and electronics markets, serving as protective enclosures for a wide range of devices and systems. Plastics play a crucial role in the manufacturing of housings, providing a lightweight, durable, and cost-effective material for a wide range of applications.
What are the benefits of using plastic for housings?
Plastic materials like polycarbonate, ABS, PBT and nylon are commonly used in the production of housings due to their excellent resistance to impact, weathering, and corrosion. Plastics also allow for greater design flexibility with assembly simplification and component reduction, allowing manufacturers to create durable cost-effective housings with a wide range of sizes, shapes, and colors.
What are common plastics used for housings?
Materials to consider for housing applications include:
|
|

The lighting market has experienced significant change over the past 10-20 years, with most incandescent, halogen, and fluorescent technologies being replaced with LED. As a result, the use of plastics has also changed, with the historical use of high temperature plastics transitioning to more specialized materials to help deflect light (optics), diffuse light (lenses), or reflect light (reflectors).
What are common plastics used for lighting applications?
Materials to consider for lighting include:
|
|

Whether a residential or industrial power system, system panels utilize a variety of components to effectively manage the distribution of power to tailored specifications. The system enclosures and panels themselves may be plastic but internally you will find switches, switch gears, breakers, terminal blocks, relays, programmable controllers, sensors, fuses, fuse holders, and cooling fans just to name a few items.
What are the benefits of using plastic for power management and distribution?
Plastic materials are widely used in these component assemblies due to technical requirements that might include tight dimensional stability, specific electrical properties, high-temperature requirements, or specific flame retardancy attributes.
What are common plastics used for power management and distribution applications?
Materials to consider for power management and distribution include:
|

Solar panels and associated componentry are a growing part of the electrical and electronics markets, serving as a renewable energy source that can be used to power a wide range of devices and systems. Plastics play an important role in the manufacturing of solar panels, particularly in the form of encapsulant films, which are used to protect the cells from moisture, dust, and other environmental factors.
What are common plastics used for solar panel systems?
Plastic encapsulants like ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) and polyvinyl butyral (PVB) are commonly used in solar panel production due to their excellent optical and mechanical properties- and ability to withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight and extreme temperatures.
What are the benefits of using plastic for solar panel systems?
Solar panel systems require a variety of engineered polymers for supporting components such as brackets, inverters, combiner boxes, bushings, and gears. Certain applications may have unique flame or electrical requirements, while most must withstand the rigors of extreme weather exposure.
Materials to consider for solar panel applications include:
|